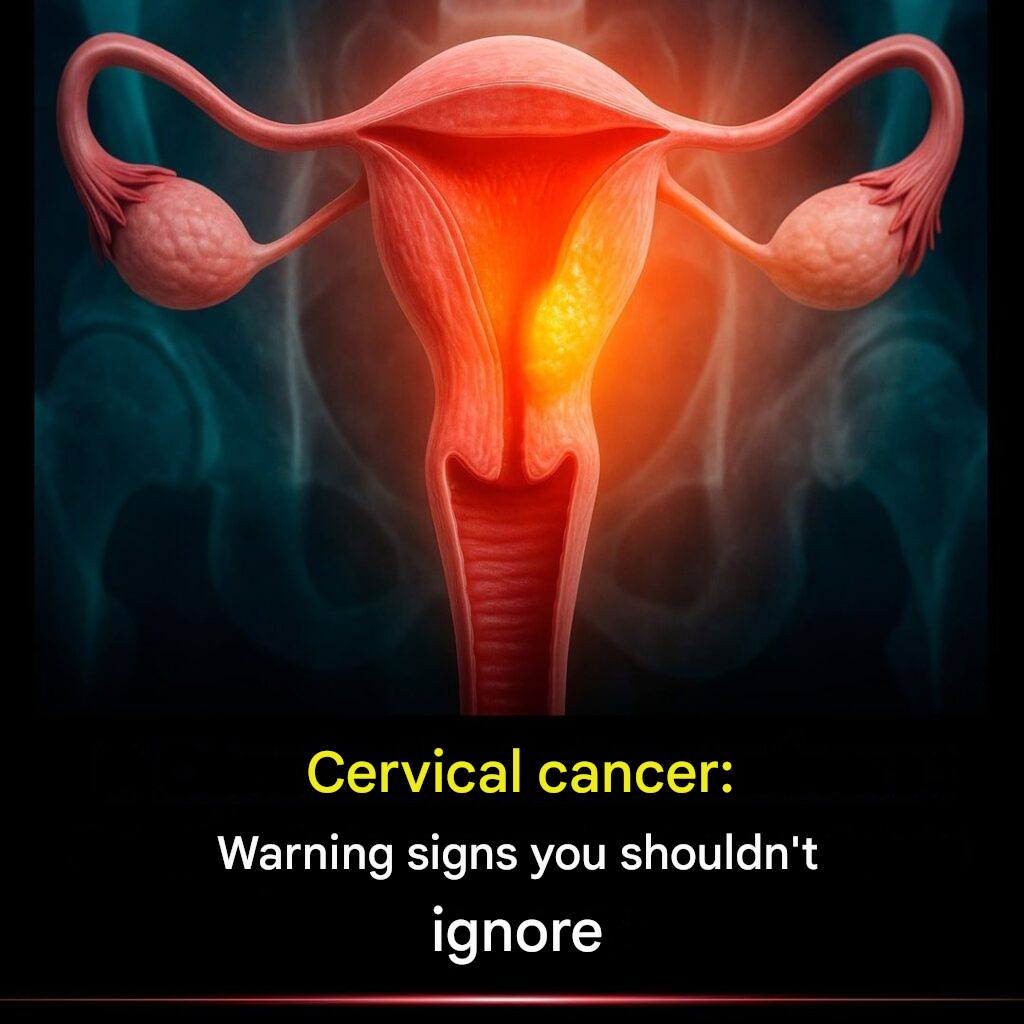
Prevention is better than cure.
Vigilance and preventive measures make all the difference. These are the steps to take:
HPV vaccine: recommended starting in adolescence, for both sexes.
Pap smear: should be performed every 3 years starting at age 25.
HPV screening: recommended between the ages of 30 and 65, and repeated every five years.
Protection during sexual intercourse: reduces the risk of infection. A healthy lifestyle—a balanced diet, physical exercise, and quitting smoking—strengthens our natural defenses.
How is an accurate diagnosis made?
Several tests have been conducted to confirm or rule out suspicions:
Cervical swab: microscopic examination of cells.
HPV detection: identification of dangerous strains.
If abnormalities are detected, a complete examination is performed using a colposcope.
Tissue sampling is taken in cases of serious doubt.
Medical imaging tests (MRI, CT scan) will be performed to assess the extent of the case if the diagnosis is positive.
See continued on the next page.